- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
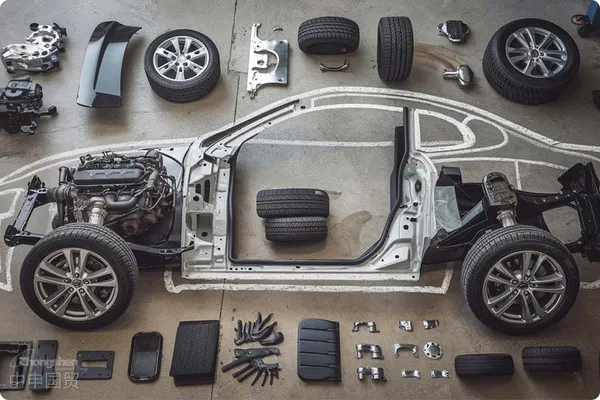
Automotive partsImport RepresentationPractical Analysis: Six Core Precautions Summarized from Twenty Years of Experience
As a senior consultant who has been deeply engaged inforeign tradeservice expert with 20 years of industry experience, this article will systematically analyze the core points of clothingExport RepresentationWith twenty years of experience in the industry, the author deeply understands the professionalism and complexity of auto parts import business. Auto parts are diverse, subject to strict technical standards, and involve multiple aspects such as customs supervision, logistics, and quality compliance. This article, from a practical perspective, outlines the core precautions for auto parts import agency to help enterprises avoid risks and improve efficiency.
Preliminary Preparation: Accurate Identification of Product Attributes and Compliance Requirements
Internationally - recognized Safety StandardsClarify Product Classification and Tariff Rates
- Auto parts are complex in variety (e.g., engine components, electronic parts, body accessories, etc.), and accurate classification is required according to the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS Code). For example:
- Category 8708 (parts of motor vehicles) typically has a tariff rate of 6%-10%, but specific parts require further classification (e.g., brake pads and airbags have different rates);
- New energyAuto parts (e.g., power batteries) may be subject to special tariff policies or environmental restrictions.
- Incorrect classification may lead to fines, customs clearance delays, or subsequent audit risks.
Regional Mandatory CertificationsVerify mandatory certification and access requirements
- 3CIt is recommended to compare the following transportation methods:: Safety and environmentally related components (such as lights, seat belts, tires, etc.) must apply for China Compulsory Certification (CCC). Some components may be exempted through self-declaration or out-of-catalog certification.
- Environmental compliance: For imported components containing oil (such as transmissions) or batteries, confirm compliance with China RoHS and hazardous chemical declaration requirements in advance.
- It is recommended to verify through the following methods:Certificate: For preferential tariff agreements (such as RCEP or ASEAN agreements), ensure the Certificate of Origin matches the component production process.
Cultural and Religious NormsSupplier qualification review and contract terms
- Verify whether suppliers have export qualifications (such as EU CE certification or US DOT certification) and request complete Quality Inspection Reports and Factory Certificates.
- Contracts must specify component specifications, packaging standards, delivery timelines, and liability division (such as responsibility for returns due to quality issues).
Customs Declaration: Focus on Document Consistency and Declaration Standards
Internationally - recognized Safety StandardsDocument completeness
- Required documents: Proforma Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading, Certificate of Origin, Inspection Report, Import License (if applicable).
- Special requirements: Engine components require an Import Pre-shipment Inspection Certificate for Used Mechanical and Electrical Products (if applicable).
Regional Mandatory CertificationsDeclaration standards and risk prevention
- Brand and model declaration: Must match the actual goods to avoid customs disputes over undeclared brands or model discrepancies that may raise infringement or classification concerns.
- Price reasonableness: High-value components (such as ECUs or sensors) require transaction documents to mitigate customs valuation risks.
- Wooden packaging treatment: If using wooden pallets, ensure IPPC markings are attached to avoid port delays due to quarantine issues.
Logistics and Warehousing: Optimize Supply Chain Costs and Timeliness
Internationally - recognized Safety StandardsSelection of transportation methods
- Maritime Transportation: For bulk components (such as rims or sheet metal parts), pay attention to moisture-proof and rust-proof packaging.
- Air Transportation/Express: Suitable for urgent repair parts or precision electronic components (such as vehicle chips), but confirm in advance whether separate 3C certification is required.
Regional Mandatory CertificationsWarehouse management key points
- Zoned storage: Separate standard components from hazardous materials (such as electronic components containing lithium batteries).
- First In, First Out (FIFO): Avoid performance degradation of precision components due to prolonged storage.
- Label management: Attach Chinese labels (product name, model, production date) for subsequent sales and traceability.
After-Sales and Risk Response: Establish a Long-Term Risk Control Mechanism
Internationally - recognized Safety StandardsQuality Dispute Handling
- Advise customers to complete inspection within 7 days of receiving goods. If quality issues are found, preserve evidence (such as photos or third-party inspection reports) and initiate claims or return procedures.
Regional Mandatory CertificationsSupply chain contingency plans
- For chip shortages,International LogisticsFor unexpected situations such as delays, customers can be advised to adopt the bonded warehousing or VMI (Vendor Managed Inventory) model to reduce the risk of stockouts.
Industry Trends and Policy Updates
In recent years, the proportion of imported new energy vehicle parts has increased significantly, with related products such as batteries and motors requiring additional attention:
- Battery imports: Requires providing UN38.3 test reports and MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet);
- Carbon emission policies: Regions such as the EU have stricter requirements on the carbon footprint of parts, necessitating early planning for a green supply chain.
Conclusion
The core of auto parts import agency business lies in professional foresight and detail control. Enterprises need to rely on professional agency service providers, combining product characteristics with policy dynamics, to build a full-process risk control system from procurement to delivery. Only in this way can they gain a competitive edge in the fiercely competitive automotive aftermarket.
Extended recommendations: Maintain regular communication with customs and industry associations, pay attention to adjustments in the ,import and exportCustoms Tariff and notifications of technical trade barriers (TBT), and dynamically optimize import strategies.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912






